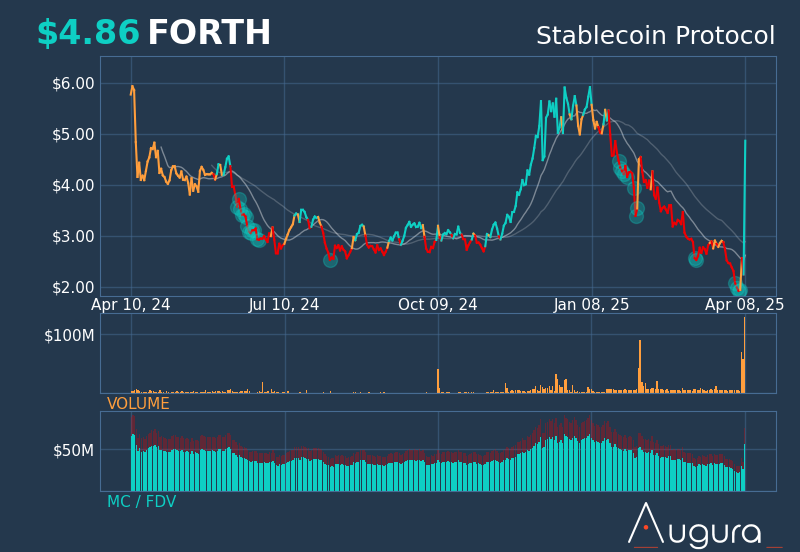
Prezzo di Ampleforth Governance

Disclaimer
OKX non fornisce raccomandazioni su investimenti o asset. Devi considerare attentamente se il trading o l'holding di asset digitali è adatto a te alla luce della tua condizione finanziaria. Consulta un professionista legale/fiscale/finanziario per domande sulla tua specifica situazione. Per ulteriori dettagli, fai riferimento ai nostri Termini di utilizzo e all'Avviso di rischio. Utilizzando il sito web di terze parti ("TPW"), accetti che qualsiasi utilizzo del TPW sarà soggetto alle condizioni del TPW e disciplinato dalle stesse. Se non espressamente dichiarato per iscritto, OKX e i suoi affiliati ("OKX") non sono associati in alcun modo al proprietario o all'operatore del TPW. Accetti che OKX non è responsabile di eventuali perdite, danni e qualsiasi altra conseguenza derivanti dall'utilizzo del TPW. Tieni presente che l'uso di un TPW potrebbe comportare una perdita o una diminuzione dei tuoi asset. Il prodotto potrebbe non essere disponibile in tutte le giurisdizioni.
Informazioni sul mercato di Ampleforth Governance
Capitalizzazione di mercato = Offerta circolante x Ultimo prezzo

Feed di Ampleforth Governance




Calcolatore FORTH


Il prezzo oggi dei Ampleforth Governance in USD
Conversioni di Ampleforth Governance popolari
| 1 FORTH in USD | 2,5500 $ |
| 1 FORTH in EUR | 2,2547 € |
| 1 FORTH in PHP | 141,79 ₱ |
| 1 FORTH in IDR | 41.947,69 Rp |
| 1 FORTH in GBP | 1,9152 £ |
| 1 FORTH in CAD | 3,5267 $ |
| 1 FORTH in AED | 9,3661 AED |
| 1 FORTH in VND | 66.216,57 ₫ |
Informazioni su Ampleforth Governance (FORTH)
- Sito web ufficiale
- White paper
- Github
- Block explorer
Domande frequenti relative al prezzo di Ampleforth Governance
Ampleforth Governance (FORTH) è un token di governance all'interno del protocollo Ampleforth, progettato per consentire agli utenti di partecipare ai processi decisionali relativi all'evoluzione del protocollo.
I token FORTH sono dedicati esclusivamente alla partecipazione alla governance. Non vengono utilizzati per pagare commissioni o effettuare transazioni all'interno della rete Ampleforth.
È possibile acquistare facilmente i token FORTH sulla piattaforma di criptovalute OKX. Il terminale di trading di criptovalute OKX include FORTH/USDT.
È inoltre possibile scambiare le proprie criptovalute esistenti, tra cui XRP (XRP), Cardano (ADA), Solana (SOL), e Chainlink (LINK), per FORTH gratuitamente e senza slittamento di prezzo utilizzando OKX Convert.
Informativa ESG
Calcolatore FORTH