En el mercado de las criptomonedas, en rápida evolución, Nuls es un proyecto innovador que pretende superar las limitaciones de las plataformas blockchain existentes. Al centrarse en la flexibilidad y la personalización, NULS ofrece una infraestructura blockchain muy adaptable. Al hacer hincapié en la modularidad, la escalabilidad y la facilidad de uso, NULS proporciona una solución integral para las empresas y los desarrolladores que buscan aprovechar el potencial de la tecnología blockchain.
¿Qué es NULS?
Nuls es una plataforma blockchain de código abierto diseñada para permitir el desarrollo y despliegue de aplicaciones descentralizadas personalizables (DApps). Su característica distintiva es su arquitectura modular, que facilita la integración perfecta de varios componentes, incluidos los mecanismos de consenso, los contratos inteligentes y los sistemas de almacenamiento. Aprovechando este enfoque modular, los desarrolladores pueden crear soluciones blockchain a medida sin necesidad de construirlo todo desde cero, lo que convierte a NULS en una plataforma versátil y eficaz para el desarrollo de blockchain.
El equipo de NULS
El equipo de NULS, dirigido por Jason Zhang como fundador y desarrollador principal, Lily Wang como cofundadora y directora de operaciones, y Reaper Ran como cofundador y líder de la comunidad, está formado por un talentoso grupo de entusiastas del blockchain y expertos del sector. Con sus diversas formaciones y experiencia, el equipo desempeña un papel crucial para garantizar el éxito del proyecto NULS. Fundado en 2017, se dedican a mantener un ecosistema resistente, seguro y fácil de usar para NULS.
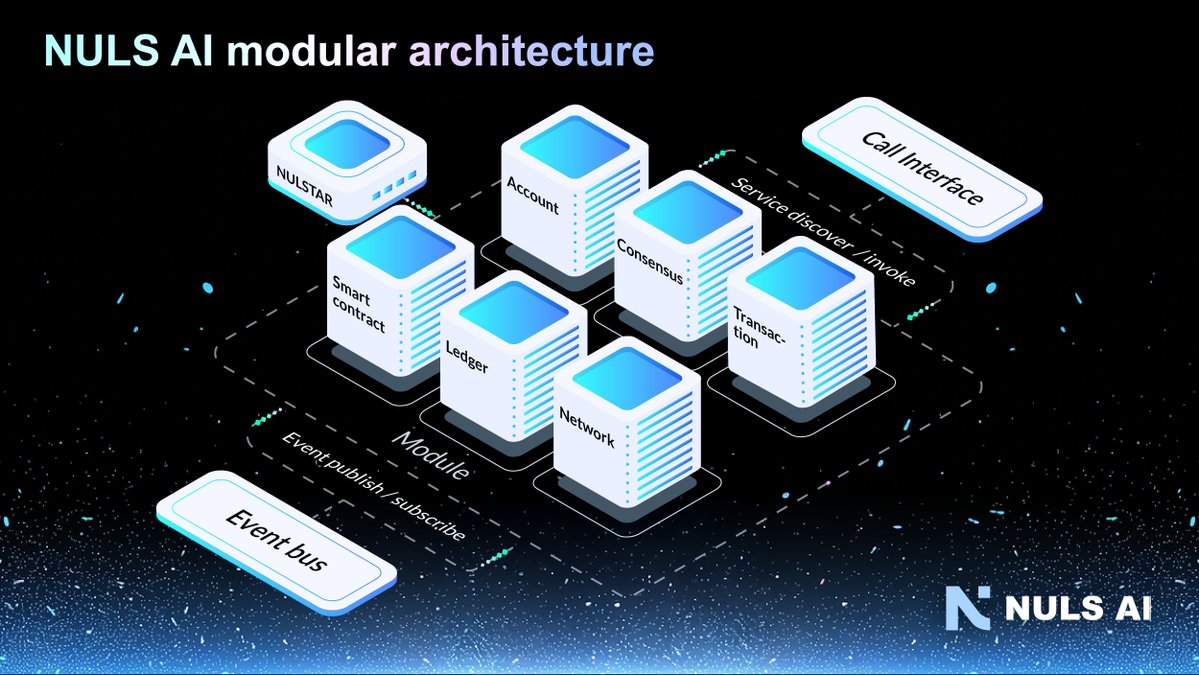
¿Cómo funciona NULS?
NULS funciona con una arquitectura modular distintiva, dividiendo la infraestructura de blockchain subyacente en varios módulos funcionales. Estos módulos engloban componentes esenciales como el mecanismo de consenso, el almacenamiento, los contratos inteligentes, etc. Al adoptar este diseño modular, NULS permite a los desarrolladores elegir y personalizar los módulos que se ajusten a sus casos de uso específicos, fomentando un ecosistema blockchain flexible y adaptable.
NULS: El token nativo de Nuls
NULS es la criptomoneda nativa de la plataforma NULS, que sirve como combustible fundamental que impulsa su red. Este token permite a los usuarios acceder a una amplia gama de funciones y servicios ofrecidos dentro de la plataforma. Además, NULS se utiliza como incentivo para los validadores y stakers de la red, desempeñando un papel crucial a la hora de garantizar la seguridad y estabilidad del ecosistema blockchain.
Tokenomics de NULS
NULS sigue un modelo de token deflacionario, limitando la oferta máxima de tokens a 100 millones. La tokenomics de NULS está diseñada para fomentar la participación activa de la comunidad, promoviendo un ecosistema justo y descentralizado. Los poseedores de tokens son recompensados por sus contribuciones a la plataforma, incluyendo hacer staking, votar y participar en mecanismos de consenso.
Casos de uso del token NULS
Los tokens NULS tienen múltiples usos dentro del ecosistema NULS. Las empresas y los desarrolladores pueden utilizar NULS para crear DApps personalizadas, establecer blockchains privadas, implementar soluciones de interoperabilidad cross-chain e incluso lanzar sus propios tokens. La flexibilidad y modularidad de NULS permiten a los usuarios explorar aplicaciones innovadoras y prácticas de la tecnología blockchain, abriendo un mundo de posibilidades para la adopción y el avance de los sistemas descentralizados.
Distribución de tokens NULS
NULS garantiza una distribución de tokens justa y generalizada mediante la asignación de tokens a diversas partes interesadas. Esto incluye la venta de tokens, los incentivos a la comunidad, el desarrollo del ecosistema, los miembros del equipo y las asociaciones estratégicas.
NULS promueve un ecosistema próspero e impulsado por la comunidad mediante la distribución de tokens entre diversos sectores.
La distribución de tokens es la siguiente:
- El 40% se destina a los inversores ángeles que han apoyado el proyecto.
- El 20% se dedica al desarrollo del proyecto, garantizando la innovación y la mejora continuas.
- El 20% de los tokens se destina a la construcción de la comunidad, fomentando el compromiso y la participación.
- El 20% se destina a asociaciones empresariales y a apoyar proyectos de terceros, ampliando el alcance y el impacto del ecosistema NULS.
NULS: Liberar el potencial de las soluciones modulares de blockchain
NULS es una prometedora plataforma blockchain que hace especial hincapié en la flexibilidad, la escalabilidad y la modularidad. Al dotar a los desarrolladores de las herramientas y recursos necesarios para construir soluciones blockchain personalizadas, NULS facilita una adopción más amplia de las tecnologías descentralizadas.
Con su equipo experimentado, su tecnología innovadora y su vibrante comunidad, NULS está preparada para desempeñar un papel importante en la configuración del futuro de las aplicaciones blockchain. A medida que el sector sigue evolucionando, NULS se mantiene firme en su compromiso de capacitar a empresas y particulares para que liberen plenamente el potencial de la tecnología blockchain.


























Sociales