Sur le marché des crypto-monnaies, qui évolue rapidement, Nuls est un projet innovant qui vise à surmonter les limites des plateformes blockchain existantes. En mettant l'accent sur la flexibilité et la personnalisation, NULS offre une infrastructure blockchain hautement adaptable. En mettant l'accent sur la modularité, l'évolutivité et la convivialité, NULS offre une solution complète aux entreprises et aux développeurs qui cherchent à exploiter le potentiel de la technologie blockchain.
Qu'est-ce que c'est NULS?
Nuls est une plateforme blockchain open-source conçue pour permettre le développement et le déploiement d'infrastructures blockchain des applications décentralisées (DApps) personnalisées. Sa caractéristique distinctive est son architecture modulaire, qui facilite l'intégration transparente de divers composants, y compris les mécanismes de consensus, les smart contracts et les systèmes de stockage. En tirant parti de cette approche modulaire, les développeurs peuvent créer des solutions de blockchain sur mesure sans avoir à tout construire à partir de zéro, ce qui fait de NULS une plateforme polyvalente et efficace pour le développement de la blockchain.
L'équipe de NULS
L'équipe de NULS, dirigée par Jason Zhang en tant que fondateur et développeur principal, Lily Wang en tant que cofondatrice et COO, et Reaper Ran en tant que cofondateur et responsable de la communauté, comprend un groupe talentueux de passionnés de la blockchain et d'experts de l'industrie. Grâce à leurs divers parcours et à leur expertise, l'équipe joue un rôle crucial dans la réussite du projet NULS. Fondée en 2017, elle se consacre au maintien d'un écosystème résilient, sécurisé et convivial pour NULS.
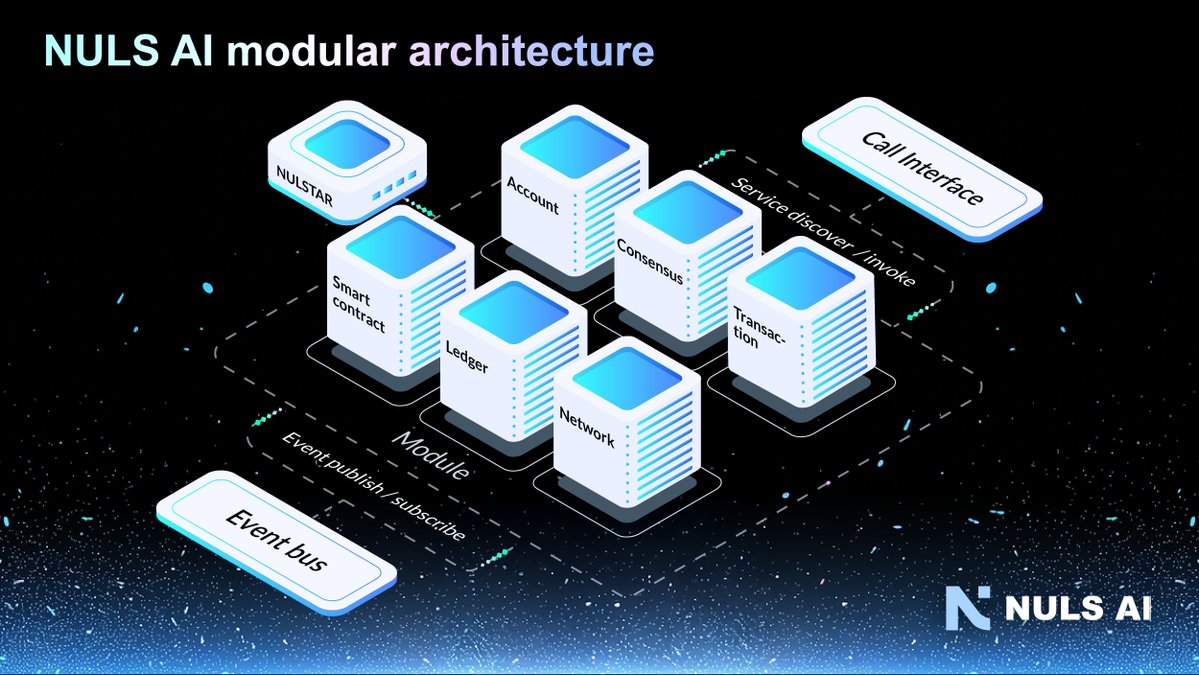
Comment fonctionne NULS?
NULS fonctionne sur une architecture modulaire distinctive, en divisant l'infrastructure blockchain sous-jacente en divers modules fonctionnels. Ces modules englobent des composants essentiels tels que le mécanisme de consensus, le stockage, les smart contracts, etc. En adoptant cette conception modulaire, NULS permet aux développeurs de choisir et de personnaliser les modules qui s'alignent sur leurs cas d'utilisation spécifiques, favorisant ainsi un écosystème de blockchain flexible et adaptable.
NULS: Le token natif de Nuls
NULS est la crypto-monnaie native de la plateforme NULS, en servant de carburant fondamental à son réseau. Ce token permet aux utilisateurs d'accéder à un large éventail de fonctionnalités et de services offerts au sein de la plateforme. En outre, NULS est utilisé comme incitation pour les validateurs et les stakers du réseau, en jouant un rôle crucial pour assurer la sécurité et la stabilité de l'écosystème de la blockchain.
La tokenomics de NULS
NULS suit un modèle des tokens déflationniste, en plafonnant l'offre maximale de tokens à 100 millions. La tokenomics de NULS est conçue pour encourager la participation active de la communauté, en promouvant un écosystème équitable et décentralisé. Les détenteurs de tokens sont récompensés pour leurs contributions à la plateforme, y compris le staking, le vote et l'engagement dans les mécanismes de consensus.
Cas d'utilisation des tokens NULS
Les tokens NULS ont de multiples cas d'utilisation au sein de l'écosystème NULS. Les entreprises et les développeurs peuvent utiliser les NULS pour créer des DApps personnalisés, établir des blockchains privées, mettre en œuvre des solutions d'interopérabilité entre chaînes et même lancer leurs propres tokens. La flexibilité et la modularité de NULS permettent aux utilisateurs d'explorer des applications innovantes et pratiques de la technologie blockchain, en ouvrant un monde de possibilités pour l'adoption et l'avancement des systèmes décentralisés.
Distribution des tokens NULS
NULS assure une distribution équitable et généralisée des tokens en attribuant des tokens à diverses parties prenantes. Cela comprend les ventes de tokens, les incitations communautaires, le développement de l'écosystème, les membres de l'équipe et les partenariats stratégiques.
NULS promeut un écosystème prospère et axé sur la communauté en distribuant des tokens dans différents secteurs.
La répartition des tokens est la suivante:
- Quarante pour cent sont alloués aux investisseurs providentiels qui ont soutenu le projet.
- Vingt pour cent sont consacrés au développement du projet, en garantissant une innovation et une amélioration continues.
- Vingt pour cent des tokens sont réservés à la construction de la communauté, en favorisant l'engagement et la participation.
- Vingt pour cent sont alloués à des partenariats commerciaux et au soutien de projets tiers, en élargissant ainsi la portée et l'impact de l'écosystème NULS.
NULS: Libérer le potentiel des solutions blockchain modulaires
NULS est une plateforme blockchain prometteuse qui met fortement l'accent sur la flexibilité, l'évolutivité et la modularité. En dotant les développeurs des outils et ressources nécessaires pour construire des solutions blockchain personnalisées, NULS facilite l'adoption plus large des technologies décentralisées.
Avec son équipe expérimentée, sa technologie innovante et sa communauté dynamique, NULS est prête à jouer un rôle important dans le façonnement de l'avenir des applications blockchain. Alors que l'industrie continue d'évoluer, NULS reste ferme dans son engagement à donner aux entreprises et aux particuliers les moyens de libérer pleinement le potentiel de la technologie blockchain.


























Données sociales