
INJ
Cours du Injective
$13,2900
-$0,05400
(-0,41 %)
Évolution du cours sur les dernières 24 heures

Que ressentez-vous pour INJ aujourd’hui ?
Donnez votre avis en ajoutant un pouce vers le haut si vous pensez que le cours Ethereum et la valeur Ethereum sont en hausse, ou un pouce en bas si vous estimez que le prix Ethereum et le ETH / USD vont baisser. Suivez l’évolution Ethereum en temps réel et consultez le Ethereum cours dollar et le Ethereum cours euro pour anticiper les tendances du marché.
Votez pour voir les résultats
Avis de non-responsabilité
Le contenu social sur cette page (« Contenu »), y compris mais sans s’y limiter les tweets et les statistiques fournis par LunarCrush, est issu de tiers et fourni « tel quel » à des fins d’information uniquement. OKX ne garantit ni la qualité ni l’exactitude du Contenu, et le Contenu ne représente pas les opinions d’OKX. Il n’est pas destiné à dispenser (i) des conseils ou recommandations en matière d’investissement ; il ne doit pas (ii) non plus être considéré comme une invitation à acheter, à vendre ni à détenir des actifs numériques, ni (iii) comme des conseils financiers, comptables, juridiques ou fiscaux. Les actifs numériques (dont les stablecoins et les NFT) présentent un niveau de risque élevé, et leur valeur peut varier considérablement. Les cours et les performances des actifs numériques ne sont pas garantis et peuvent changer sans préavis.</br></br>OKX ne fournit aucune recommandation en matière d’investissement ou d’actif. Évaluez attentivement votre situation financière pour déterminer si vous êtes en mesure de détenir ou de trader des actifs numériques. Demandez conseil auprès de votre expert juridique, fiscal ou en investissement pour toute question portant sur votre situation personnelle. Pour plus de détails, consultez nos <a href="/help/terms-of-service">Conditions d’utilisation</a> et notre <a href="/help/risk-compliance-disclosure">Avertissement sur les risques</a>. En utilisant le site Web tiers (« SWT »), vous acceptez que toute utilisation du SWT soit soumise et régie par les conditions du SWT. Sauf mention écrite expresse, OKX et ses sociétés affiliées (« OKX ») ne sont en aucun cas associées au propriétaire ou à l’exploitant du SWT. Vous acceptez qu’OKX ne soit responsable d’aucune perte, d’aucun dommage et d’aucune autre conséquence découlant de votre utilisation du SWT. Sachez que l’utilisation d’un SWT peut déboucher sur la perte ou la baisse de vos actifs. Le produit peut être indisponible dans certaines juridictions.
Infos sur le marché du Injective
Cap. boursière
La cap. boursière est calculée en multipliant l’offre en circulation d’un jeton par son dernier cours.
Cap. boursière = offre en circulation × dernier cours
Cap. boursière = offre en circulation × dernier cours
Approvisionnement en circulation
La quantité totale d’un jeton qui est accessible au public sur le marché.
Classement de cap. boursière
La position d’un jeton dans le classement par cap. boursière.
Sommet historique
Cours le plus élevé atteint par un jeton au cours de son historique de trading.
Minimum historique
Cours le plus bas atteint par un jeton au cours de son historique de trading.
Cap. boursière
$1,30B
Approvisionnement en circulation
97 727 220 INJ
97,72 % de
100 000 000 INJ
Classement de cap. boursière
54
Audits

Dernier audit : 1 sept. 2020
Pic sur 24 h
$14,0550
Creux sur 24 h
$13,0740
Sommet historique
$53,2000
-75,02 % (-$39,9100)
Dernière mise à jour : 14 mars 2024
Minimum historique
$6,3420
+109,55 % (+$6,9480)
Dernière mise à jour : 7 avr. 2025
Flux de Injective
Le contenu suivant provient de .

Pryzm
Déléguer aux validateurs de Pryzm débloque des récompenses supplémentaires chaque semaine : gagnez vos retours de staking réguliers et $PRYZM airdrops de jetons !
✅ Enregistrez votre adresse :
✅ Réclamation hebdomadaire sur la page du portfolio
Merci de nous soutenir !
$ATOM $OSMO $TIA $LUNA $DYM $INJ
Afficher l’original
12,12 k
47

ProfessorAstrones
Ces 10 #altcoins favoris feront la prochaine génération de millionnaires
Je rendrai mes adeptes riches lors de cette bullrun, tout comme je me suis enrichi lors de la dernière bullrun
1 : $INJ
Cible : 5x à 10x
2 : $FET
Cible : 8x à 12x
3 : $RLC
Cible : 8x à 12x
4 : $ALGO
Cible : 10x à 14x
5 : $WOO
Cible : 10x à 14x
6 : $ARB
Cible : 12x à 16x
7 : $ZIG
Cible : 15x à 20x
8 : $COTI
Cible : 15x à 20x
9 : $FLOKI
Cible : 30x à 40x
10 : $MOG
Cible : 30 à 50x
J’espère que vous avez apprécié cette liste et faites-moi savoir si j’ai manqué quelque chose !
Quel jeton manque à votre portefeuille ? #crypto
Ajoutez ce tweet à vos favoris et revenez dans quelques mois pour voir combien de X vous avez manqués.
Je vous promets que vous ne regretterez pas de m’avoir suivi.
Afficher l’original70,44 k
330

Santiment
🧑 💻 Voici les 10 meilleurs projets DeFi de crypto par développement. Les indicateurs directionnels représentent le positionnement de chaque projet depuis le mois dernier :
➡️ 1) @chainlink $LINK 🥇
📈 2) @deepbookonsui $DEEP 🥈
📉 3) @defichain $DFI 🥉
➡️ 4) @synthetix_io $SNX
📈 5) @lidofinance $LDO
📈 6) @liquityprotocol $LQTY
📉 7) @coinbase $CBBTC
📈 8) @injective $INJ
📈 9) @babylonlabs_io $BABY
➡️ 10) @uniswap $UNI
En savoir plus sur la méthodologie de @santimentfeed pour couvrir les activités de développement de plus de 4 000 projets :
Afficher l’original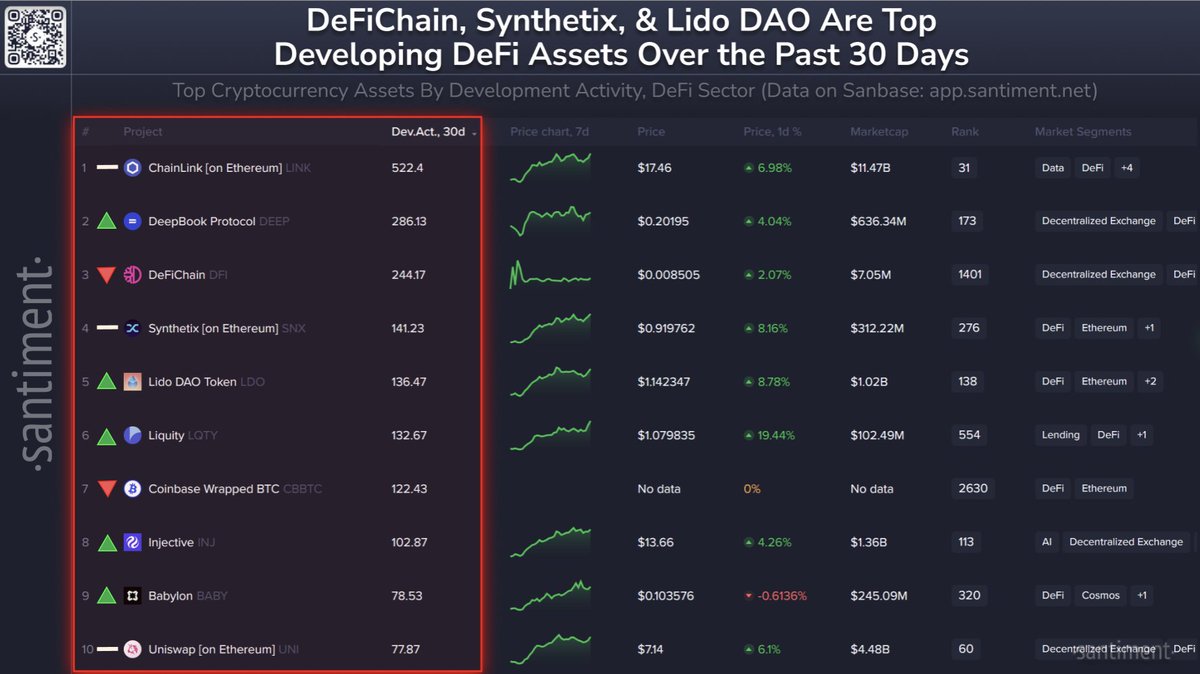
58,59 k
181
Calculateur INJ


Performance du cours de Injective en USD
Le cours de Injective est actuellement de $13,2900. Au cours des dernières 24 heures, la valeur Injective a a diminué de -0,40 %. Il a actuellement une offre en circulation de 97 727 220 INJ et une offre maximale de 100 000 000 INJ, ce qui lui donne une capitalisation boursière totalement diluée de $1,30B. Actuellement, le jeton Injective occupe la 54 position du classement par capitalisation boursière. Le cours Injective/USD est mis à jour en temps réel.
Aujourd'hui
-$0,05400
-0,41 %
7 jours
+$3,7130
+38,76 %
30 jours
+$5,0640
+61,56 %
3 mois
-$1,8300
-12,11 %
Conversions de Injective populaires
Dernière mise à jour : 14/05/2025 22:07
| 1 INJ en USD | 13,3560 $ |
| 1 INJ en EUR | 11,9069 € |
| 1 INJ en PHP | 746,16 ₱ |
| 1 INJ en IDR | 221 052,6 Rp |
| 1 INJ en GBP | 10,0301 £ |
| 1 INJ en CAD | 18,6429 $ |
| 1 INJ en AED | 49,0573 AED |
| 1 INJ en VND | 346 459,1 ₫ |
À propos du Injective (INJ)
La notation fournie correspond à une notation agrégée qui est collectée par OKX à partir des sources fournies. Elle n’est indiquée qu’à titre indicatif. OKX ne garantit ni la qualité ni l’exactitude des notations. Elle n’est pas destinée à dispenser (i) des conseils ou recommandations en matière d’investissement ; elle ne doit pas (ii) non plus être considérée comme une invitation à acheter, à vendre ni à détenir des actifs numériques, ni (iii) comme des conseils financiers, comptables, juridiques ou fiscaux. Les actifs numériques (dont les stablecoins et les NFT) présentent un niveau de risque élevé ; leur valeur peut varier considérablement, voire devenir nulle. Les prix et les performances des actifs numériques ne sont pas garantis et peuvent changer sans préavis. Vos actifs numériques ne sont pas couverts par une assurance contre les pertes potentielles. Les rendements historiques ne constituent pas un indicateur des rendements futurs. OKX ne garantit aucun rendement, ni le remboursement du capital et des intérêts. Évaluez attentivement votre situation financière pour déterminer si vous êtes en mesure de détenir des actifs numériques ou de réaliser des activités de trading. Demandez conseil auprès de votre expert juridique/fiscal/en investissement pour toute question portant sur votre propre situation.
Afficher plus
- Site web officiel
- Github
- Explorateur de blocs
À propos des sites Web tiers
À propos des sites Web tiers
En utilisant le site web tiers (« SWT »), vous acceptez que toute utilisation du SWT soit sujette aux conditions du SWT et gouvernée par celles-ci. Sauf mention écrite expresse, OKX et ses affiliés (« OKX ») ne sont en aucun cas associés au propriétaire ni à l’opérateur du SWT. Vous acceptez le fait qu’OKX ne soit pas responsable des pertes, dommages ni de toutes autres conséquences découlant de votre utilisation du SWT. Veuillez noter que l’utilisation d’un SWT peut entraîner une perte ou une diminution de vos actifs.
FAQ Injective
Combien vaut 1 Injective aujourd’hui ?
Actuellement, 1 Injective vaut $13,2900. Vous recherchez des informations sur les mouvements de prix du token Injective ? Vous êtes au bon endroit ! Découvrez les graphiques les plus récents sur le token Injective et tradez de manière responsable avec OKX.
Qu'est-ce que la cryptomonnaie ?
Les cryptomonnaies, telles que les Injective, sont des actifs numériques fonctionnant sur un registre public appelé blockchain. En savoir plus sur les jetons proposés sur OKX et leurs différents attributs, notamment le cours en direct et les graphiques en temps réel.
Quand la cryptomonnaie a-t-elle été inventée ?
En raison de la crise financière de 2008, l’intérêt porté à la finance décentralisée a explosé. Le Bitcoin offrait une solution novatrice en tant qu’actif numérique sécurisé sur un réseau décentralisé. De nombreux jetons tels que les Injective ont également été créés depuis lors.
Le cours du Injective va-t-il augmenter aujourd'hui ?
Consultez notre Page de prédiction des cours de Injective pour prévoir les cours à venir et déterminer vos objectifs de cours.
Déclaration ESG
Les réglementations ESG (approche environnementale, sociale et de gouvernance) relatives aux actifs crypto visent à réduire leur impact environnemental (par exemple : l'extraction minière à forte intensité énergétique), à promouvoir la transparence et à garantir des pratiques de gouvernance éthiques afin d'aligner le secteur des cryptos sur des objectifs plus larges en matière de durabilité et de société. Ces réglementations encouragent le respect de normes qui atténuent les risques et favorisent la confiance dans les actifs numériques.
Détails de l’actif
Nom
OKcoin Europe LTD
Identifiant de l’entité juridique concernée
54930069NLWEIGLHXU42
Nom de l’actif crypto
Injective Token
Mécanisme de consensus
Injective Token is present on the following networks: binance_smart_chain, cosmos, ethereum.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) uses a hybrid consensus mechanism called Proof of Staked Authority (PoSA), which combines elements of Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and Proof of Authority (PoA). This method ensures fast block times and low fees while maintaining a level of decentralization and security. Core Components 1. Validators (so-called “Cabinet Members”): Validators on BSC are responsible for producing new blocks, validating transactions, and maintaining the network’s security. To become a validator, an entity must stake a significant amount of BNB (Binance Coin). Validators are selected through staking and voting by token holders. There are 21 active validators at any given time, rotating to ensure decentralization and security. 2. Delegators: Token holders who do not wish to run validator nodes can delegate their BNB tokens to validators. This delegation helps validators increase their stake and improves their chances of being selected to produce blocks. Delegators earn a share of the rewards that validators receive, incentivizing broad participation in network security. 3. Candidates: Candidates are nodes that have staked the required amount of BNB and are in the pool waiting to become validators. They are essentially potential validators who are not currently active but can be elected to the validator set through community voting. Candidates play a crucial role in ensuring there is always a sufficient pool of nodes ready to take on validation tasks, thus maintaining network resilience and decentralization. Consensus Process 4. Validator Selection: Validators are chosen based on the amount of BNB staked and votes received from delegators. The more BNB staked and votes received, the higher the chance of being selected to validate transactions and produce new blocks. The selection process involves both the current validators and the pool of candidates, ensuring a dynamic and secure rotation of nodes. 5. Block Production: The selected validators take turns producing blocks in a PoA-like manner, ensuring that blocks are generated quickly and efficiently. Validators validate transactions, add them to new blocks, and broadcast these blocks to the network. 6. Transaction Finality: BSC achieves fast block times of around 3 seconds and quick transaction finality. This is achieved through the efficient PoSA mechanism that allows validators to rapidly reach consensus. Security and Economic Incentives 7. Staking: Validators are required to stake a substantial amount of BNB, which acts as collateral to ensure their honest behavior. This staked amount can be slashed if validators act maliciously. Staking incentivizes validators to act in the network's best interest to avoid losing their staked BNB. 8. Delegation and Rewards: Delegators earn rewards proportional to their stake in validators. This incentivizes them to choose reliable validators and participate in the network’s security. Validators and delegators share transaction fees as rewards, which provides continuous economic incentives to maintain network security and performance. 9. Transaction Fees: BSC employs low transaction fees, paid in BNB, making it cost-effective for users. These fees are collected by validators as part of their rewards, further incentivizing them to validate transactions accurately and efficiently.
The Cosmos network uses the Cosmos SDK, a modular framework that enables developers to build custom, application-specific blockchains. Cosmos SDK chains rely on Tendermint Core, a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus engine that supports interoperability and fast transaction finality. Core Components: 1. Tendermint BFT Consensus with Proof of Stake: Validator Selection: Cosmos validators are selected based on the amount of ATOM they stake or receive from delegators. These validators participate in block proposal and validation through a two-thirds majority voting system. Security Threshold: Tendermint BFT ensures network security as long as fewer than one-third of validators act maliciously. 2. Modular Cosmos SDK Framework: Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC): The Cosmos SDK supports IBC, allowing seamless interoperability between Cosmos-based blockchains. Application Blockchain Interface (ABCI): This interface separates the consensus layer from the application layer, enabling developers to implement custom logic without modifying the consensus engine.
The Ethereum network uses a Proof-of-Stake Consensus Mechanism to validate new transactions on the blockchain. Core Components 1. Validators: Validators are responsible for proposing and validating new blocks. To become a validator, a user must deposit (stake) 32 ETH into a smart contract. This stake acts as collateral and can be slashed if the validator behaves dishonestly. 2. Beacon Chain: The Beacon Chain is the backbone of Ethereum 2.0. It coordinates the network of validators and manages the consensus protocol. It is responsible for creating new blocks, organizing validators into committees, and implementing the finality of blocks. Consensus Process 1. Block Proposal: Validators are chosen randomly to propose new blocks. This selection is based on a weighted random function (WRF), where the weight is determined by the amount of ETH staked. 2. Attestation: Validators not proposing a block participate in attestation. They attest to the validity of the proposed block by voting for it. Attestations are then aggregated to form a single proof of the block’s validity. 3. Committees: Validators are organized into committees to streamline the validation process. Each committee is responsible for validating blocks within a specific shard or the Beacon Chain itself. This ensures decentralization and security, as a smaller group of validators can quickly reach consensus. 4. Finality: Ethereum 2.0 uses a mechanism called Casper FFG (Friendly Finality Gadget) to achieve finality. Finality means that a block and its transactions are considered irreversible and confirmed. Validators vote on the finality of blocks, and once a supermajority is reached, the block is finalized. 5. Incentives and Penalties: Validators earn rewards for participating in the network, including proposing blocks and attesting to their validity. Conversely, validators can be penalized (slashed) for malicious behavior, such as double-signing or being offline for extended periods. This ensures honest participation and network security.
Mécanismes d’incitation et frais applicables
Injective Token is present on the following networks: binance_smart_chain, cosmos, ethereum.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) uses the Proof of Staked Authority (PoSA) consensus mechanism to ensure network security and incentivize participation from validators and delegators. Incentive Mechanisms 1. Validators: Staking Rewards: Validators must stake a significant amount of BNB to participate in the consensus process. They earn rewards in the form of transaction fees and block rewards. Selection Process: Validators are selected based on the amount of BNB staked and the votes received from delegators. The more BNB staked and votes received, the higher the chances of being selected to validate transactions and produce new blocks. 2. Delegators: Delegated Staking: Token holders can delegate their BNB to validators. This delegation increases the validator's total stake and improves their chances of being selected to produce blocks. Shared Rewards: Delegators earn a portion of the rewards that validators receive. This incentivizes token holders to participate in the network’s security and decentralization by choosing reliable validators. 3. Candidates: Pool of Potential Validators: Candidates are nodes that have staked the required amount of BNB and are waiting to become active validators. They ensure that there is always a sufficient pool of nodes ready to take on validation tasks, maintaining network resilience. 4. Economic Security: Slashing: Validators can be penalized for malicious behavior or failure to perform their duties. Penalties include slashing a portion of their staked tokens, ensuring that validators act in the best interest of the network. Opportunity Cost: Staking requires validators and delegators to lock up their BNB tokens, providing an economic incentive to act honestly to avoid losing their staked assets. Fees on the Binance Smart Chain 5. Transaction Fees: Low Fees: BSC is known for its low transaction fees compared to other blockchain networks. These fees are paid in BNB and are essential for maintaining network operations and compensating validators. Dynamic Fee Structure: Transaction fees can vary based on network congestion and the complexity of the transactions. However, BSC ensures that fees remain significantly lower than those on the Ethereum mainnet. 6. Block Rewards: Incentivizing Validators: Validators earn block rewards in addition to transaction fees. These rewards are distributed to validators for their role in maintaining the network and processing transactions. 7. Cross-Chain Fees: Interoperability Costs: BSC supports cross-chain compatibility, allowing assets to be transferred between Binance Chain and Binance Smart Chain. These cross-chain operations incur minimal fees, facilitating seamless asset transfers and improving user experience. 8. Smart Contract Fees: Deployment and Execution Costs: Deploying and interacting with smart contracts on BSC involves paying fees based on the computational resources required. These fees are also paid in BNB and are designed to be cost-effective, encouraging developers to build on the BSC platform.
The Cosmos network incentivizes both validators and delegators to secure the network through staking rewards, funded by transaction fees and newly minted ATOM. Incentive Mechanisms: 1. Staking Rewards for Validators and Delegators: ATOM Rewards: Validators earn staking rewards in ATOM tokens for participating in consensus, with rewards shared with delegators who stake ATOM through delegation. 2. Slashing for Accountability: Penalties for Misconduct: Validators who act maliciously, such as double-signing or staying offline, face slashing penalties, which remove a portion of their staked ATOM. Delegators may also experience slashing if their chosen validator is penalized, encouraging careful selection of trustworthy validators. Applicable Fees: 1. Transaction Fees: User-Paid Fees in ATOM: All transactions on the Cosmos Hub incur fees paid in ATOM, compensating validators for transaction processing and helping to prevent network spam. 2. Customizable Fee Model: Custom Token Fees: Cosmos SDK allows individual chains to define their own transaction fees in tokens other than ATOM, supporting varied application requirements within the ecosystem.
Ethereum, particularly after transitioning to Ethereum 2.0 (Eth2), employs a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism to secure its network. The incentives for validators and the fee structures play crucial roles in maintaining the security and efficiency of the blockchain. Incentive Mechanisms 1. Staking Rewards: Validator Rewards: Validators are essential to the PoS mechanism. They are responsible for proposing and validating new blocks. To participate, they must stake a minimum of 32 ETH. In return, they earn rewards for their contributions, which are paid out in ETH. These rewards are a combination of newly minted ETH and transaction fees from the blocks they validate. Reward Rate: The reward rate for validators is dynamic and depends on the total amount of ETH staked in the network. The more ETH staked, the lower the individual reward rate, and vice versa. This is designed to balance the network's security and the incentive to participate. 2. Transaction Fees: Base Fee: After the implementation of Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP) 1559, the transaction fee model changed to include a base fee that is burned (i.e., removed from circulation). This base fee adjusts dynamically based on network demand, aiming to stabilize transaction fees and reduce volatility. Priority Fee (Tip): Users can also include a priority fee (tip) to incentivize validators to include their transactions more quickly. This fee goes directly to the validators, providing them with an additional incentive to process transactions efficiently. 3. Penalties for Malicious Behavior: Slashing: Validators face penalties (slashing) if they engage in malicious behavior, such as double-signing or validating incorrect information. Slashing results in the loss of a portion of their staked ETH, discouraging bad actors and ensuring that validators act in the network's best interest. Inactivity Penalties: Validators also face penalties for prolonged inactivity. This ensures that validators remain active and engaged in maintaining the network's security and operation. Fees Applicable on the Ethereum Blockchain 1. Gas Fees: Calculation: Gas fees are calculated based on the computational complexity of transactions and smart contract executions. Each operation on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) has an associated gas cost. Dynamic Adjustment: The base fee introduced by EIP-1559 dynamically adjusts according to network congestion. When demand for block space is high, the base fee increases, and when demand is low, it decreases. 2. Smart Contract Fees: Deployment and Interaction: Deploying a smart contract on Ethereum involves paying gas fees proportional to the contract's complexity and size. Interacting with deployed smart contracts (e.g., executing functions, transferring tokens) also incurs gas fees. Optimizations: Developers are incentivized to optimize their smart contracts to minimize gas usage, making transactions more cost-effective for users. 3. Asset Transfer Fees: Token Transfers: Transferring ERC-20 or other token standards involves gas fees. These fees vary based on the token's contract implementation and the current network demand.
Début de la période à laquelle se rapporte la déclaration
2024-04-20
Fin de la période à laquelle se rapporte la déclaration
2025-04-20
Rapport sur l'énergie
Consommation énergétique
1470.57158 (kWh/a)
Sources de consommation d’énergie et méthodologies
The energy consumption of this asset is aggregated across multiple components:
To determine the energy consumption of a token, the energy consumption of the network(s) binance_smart_chain, cosmos, ethereum is calculated first. Based on the crypto asset's gas consumption per network, the share of the total consumption of the respective network that is assigned to this asset is defined. When calculating the energy consumption, we used - if available - the Functionally Fungible Group Digital Token Identifier (FFG DTI) to determine all implementations of the asset of question in scope and we update the mappings regulary, based on data of the Digital Token Identifier Foundation.
Calculateur INJ




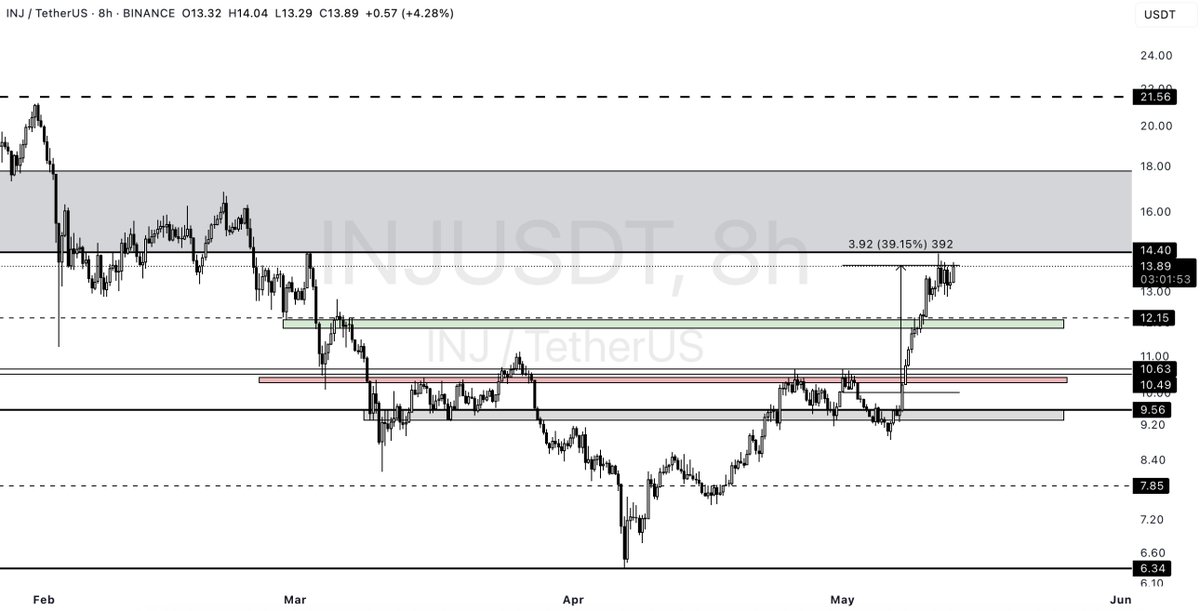
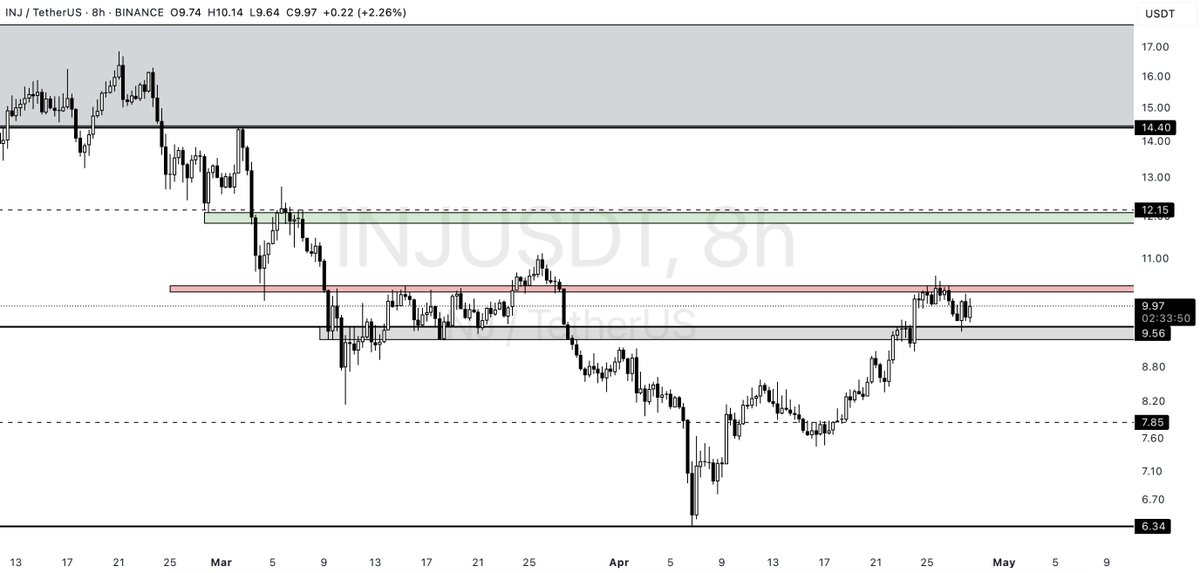













Données sociales